Word Embedding and Siamese Network
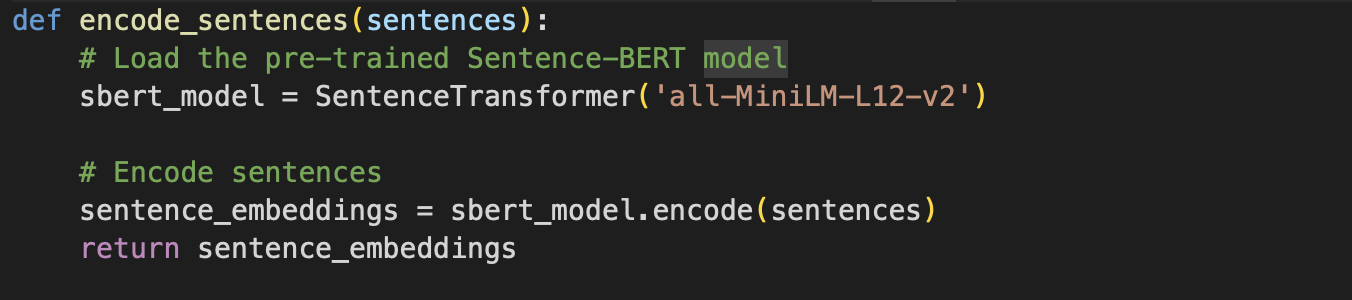
We employed Word2Vec for sentence embedding which is pivotal technique in natural language processing (NLP) for generating distributed representations of words in a continuous vector space. Its objective is to embed words such that semantically similar words are close together in the vector space, enabling machines to grasp semantic relationships between words. Word2Vec operates through two models: Continuous Bag of Words (CBOW) and Skip-gram. CBOW predicts a target word from its surrounding context, whereas Skip-gram predicts surrounding words given a target word.

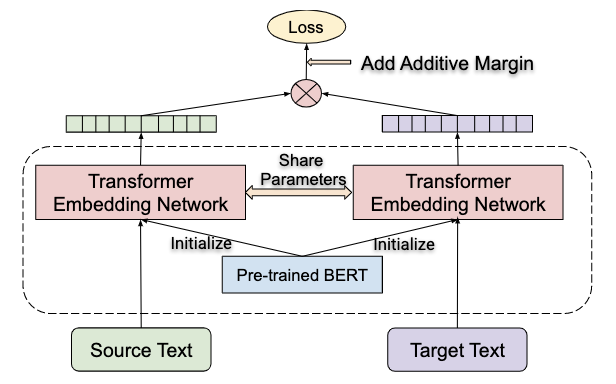
We have used a Siamese network for our model. A Siamese network is a neural architecture designed to determine the similarity or dissimilarity between two input samples, making it ideal for tasks like paraphrase detection. In the context of paraphrase identification, each branch of the Siamese network processes a different input sentence. The network employs identical neural network components for both branches, typically utilizing LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) layers to capture sequential dependencies in sentences. During training, the network learns to embed sentences into fixed-dimensional vectors in such a way that similar sentences have vectors closer together in the embedding space, while dissimilar ones are farther apart. This process is guided by a contrastive loss function that penalizes the model when it incorrectly predicts the similarity between pairs.
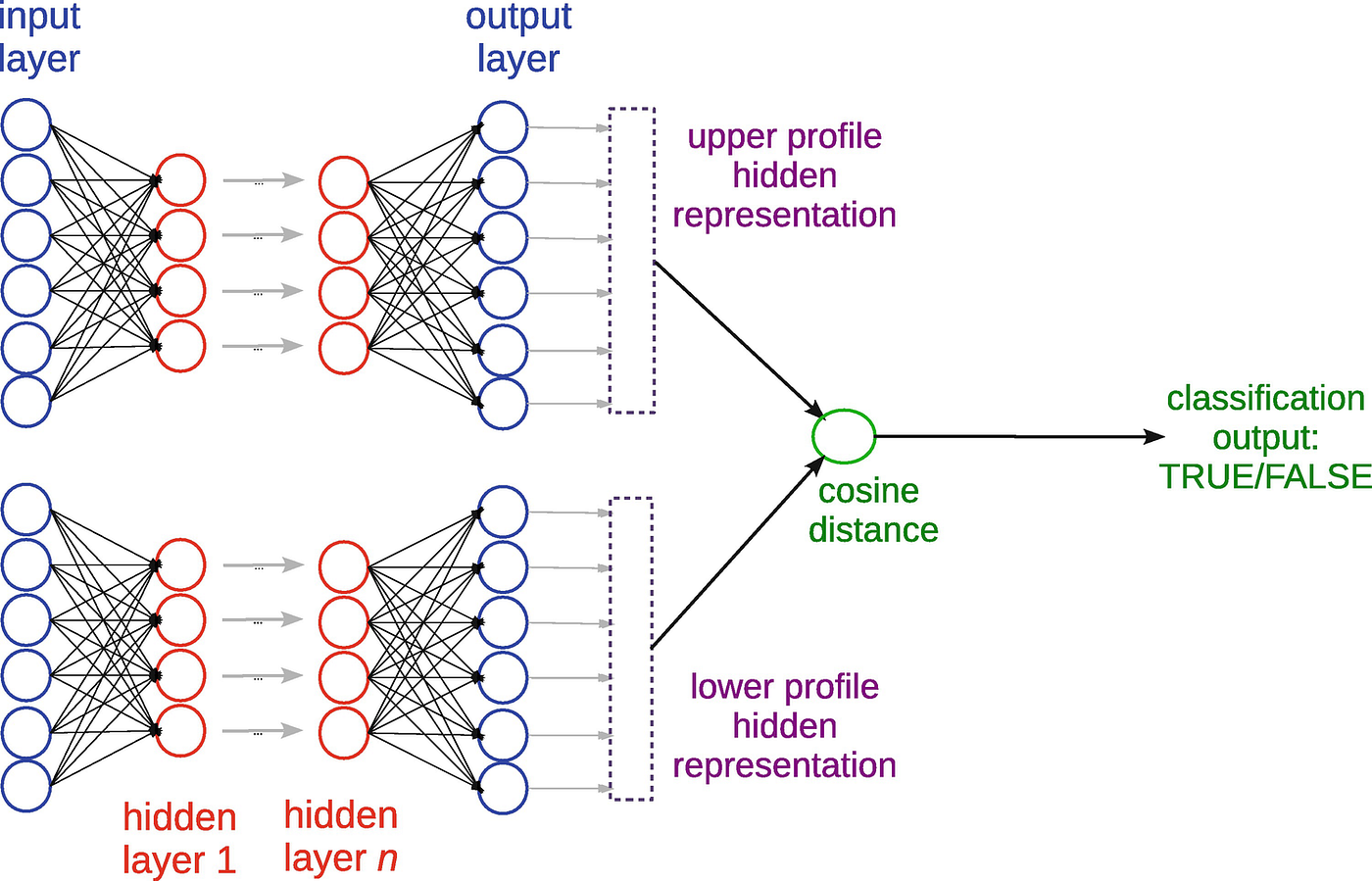

The contrastive loss function computes a penalty based on the similarity or dissimilarity of pairs of examples, such as sentences in paraphrase detection or images in similarity tasks. For each pair, labeled as either similar or dissimilar, the loss function ensures that similar pairs have embeddings with small distances, typically measured by Euclidean distance or cosine similarity. Conversely, dissimilar pairs should have embeddings that exceed a specified margin to minimize the loss.
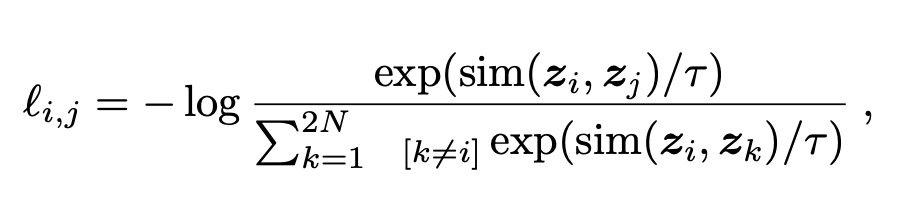

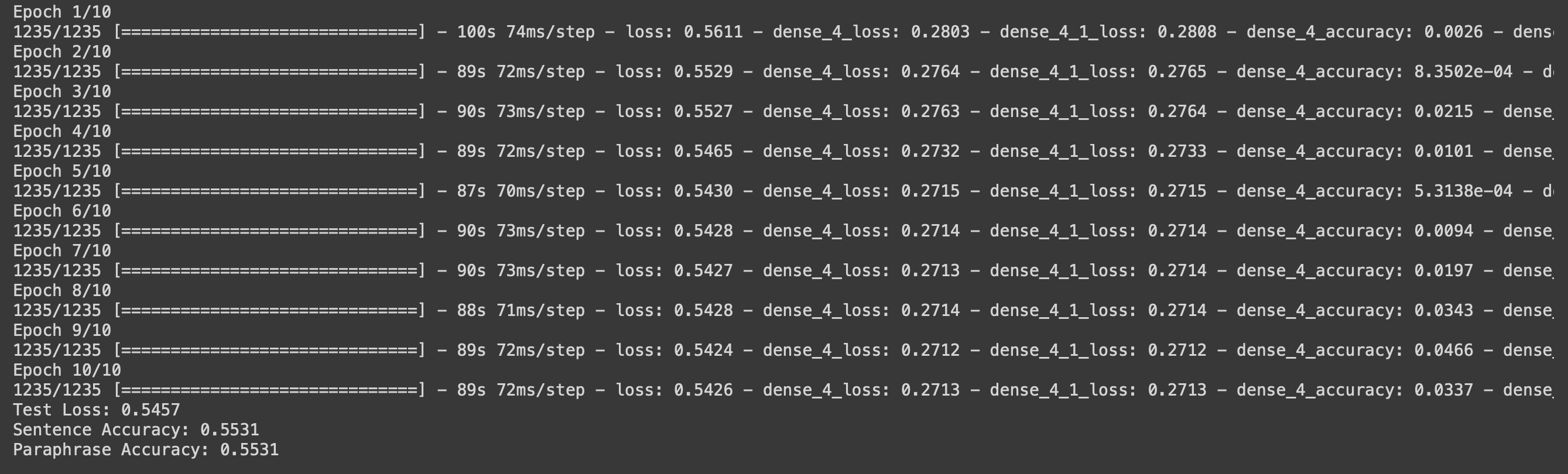
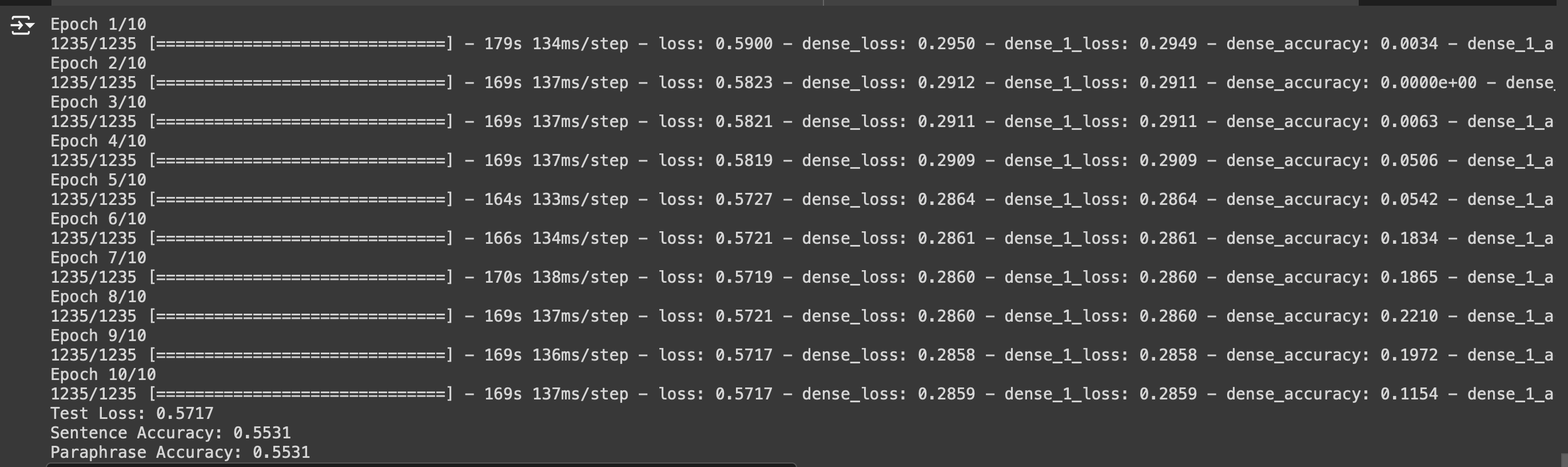
This model achieved an accuracy of 35%.